How to Read GIA Diamond Report Like a Gemologist
A diamond certification provides peace of mind and ensures you can make your purchase with confidence.

If you’re considering buying diamonds larger than 0.18 carats, certification is essential and should never be overlooked.
Certifications from respected institutions like GIA or HRD act as a safeguard, confirming that the diamond you’re purchasing meets the standards you’re looking for. Additionally, these certified diamonds are evaluated according to trusted global standards.
However, not all certified diamonds are created equal. Many buyers may not fully understand how to read a certification, which can lead to mistakenly purchasing a diamond that doesn’t meet their expectations.
That’s why we’ve written this article—to share our expertise and help you confidently read certifications and make informed decisions when investing in diamonds.
At Above Diamond, we believe knowledge is power. The more you understand about diamonds, the more assured you’ll feel when making your purchase.
4 Advantages of Buying a Certified Diamond
1. Buy Diamonds Without Worry


If you’re like most buyers, identifying real diamonds from imitations with just the naked eye can be tricky. Without proper knowledge, you could end up overpaying for a synthetic diamond or missing out on a great deal.
Technology has advanced to the point where scientists can now create “lab-grown” diamonds, known as CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) diamonds, which are so close to natural diamonds that even experts may struggle to distinguish between them. Unlike CZ or Russian synthetic diamonds, these are much harder to identify as fake.
GIA has even introduced a new certification specifically for these lab-grown diamonds, clearly stating “GIA Synthetic Diamond Report” in silver-grey text, as shown below:


While synthetic diamonds can be stunning, they lack the history and natural allure of diamonds that formed over billions of years. This is why their market value is significantly lower than that of natural diamonds.
When you purchase a certified natural diamond, you’ll know exactly where it came from, adding value and confidence to your investment. Certification ensures the diamond has been ethically sourced and holds its natural charm.
This is why certification is a key part of any diamond purchase.
2. You Get What You Pay For


When buying a diamond without certification, you’re relying entirely on the word of the seller. For instance, a vendor might claim your diamond has an E color grade when in reality, it’s an F grade—resulting in a significant price difference that’s almost impossible to detect with the naked eye.
That’s why choosing a GIA or HRD certified diamond is essential. These reports provide a clear, accurate breakdown of the 4C’s of Diamonds—ensuring transparency. You can rest easy knowing that professionals have meticulously graded your diamond in the lab.
To verify that the certification matches your diamond, simply check the laser inscription on the diamond’s edge, which corresponds with the report number.
3. Easier to Compare Value


When you have all the key characteristics of your diamond documented, it becomes much easier to compare value.
For example, if you’re looking for a 1 carat diamond with an E color grade and VVS Clarity, and you come across two diamonds priced the same—one with a Triple Excellent cut and the other with 2 Excellent and 1 Very Good—you’ll immediately know that the Triple Excellent diamond offers better value.
In contrast, a diamond without certification may seem cheaper at first, but you could end up paying more for a lower-quality stone.
4. Easy Purchase, Quick Resale


When you purchase a certified diamond, not only do you buy with confidence, but you also make your future resale process significantly easier. Certified diamonds retain their value much better than uncertified stones, especially when you decide to upgrade your diamond down the road.
As time goes on, many people reach a point where they want to enhance their jewelry collection—perhaps upgrading to a larger carat weight or a higher-quality diamond. In these cases, reselling your previous diamond becomes part of the process.
In the second-hand market, a diamond with proper certification holds much more value. Much like a luxury timepiece with original documentation or a branded handbag with proof of authenticity, the certification provides reassurance to potential buyers. It guarantees the diamond’s quality and makes it easier for them to assess the value.
If your diamond doesn’t come with certification, the potential buyer might doubt its quality or even assume it’s of a lower grade than it truly is. This uncertainty can drastically reduce the resale price.
By choosing a certified diamond, you not only enjoy the peace of mind during your initial purchase, but you also secure a higher value in the future, should you ever decide to resell it. A small investment in certification upfront can make a significant difference in both long-term value and ease of resale.
So, if you’re thinking about the future—whether for investment purposes or for upgrading your jewelry—it’s always wise to opt for a certified diamond.
GIA Certified Diamonds: The International Standard
There are two types of GIA diamond certifications:
GIA Diamond Grading Report


The GIA Diamond Grading Report is the most comprehensive type of certification issued by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), widely regarded as the gold standard in diamond certification. This report is typically issued for diamonds that are 1 carat or larger.
What sets the GIA Diamond Grading Report apart is the level of detail it provides. It includes a full assessment of the diamond’s 4C’s—Carat weight, Color, Clarity, and Cut. Additionally, the report contains a diagram, which clearly marks the location of any inclusions or blemishes within the diamond. This feature allows you to see where the diamond’s unique imperfections are situated.
The report will often come with a laser inscription of the report number on the diamond’s girdle, ensuring that the certification matches the exact diamond it was issued for. This inscription can be verified on the GIA website, allowing you to check the diamond’s details at any time.
The GIA Diamond Grading Report is especially valuable because of its strict standards. GIA is known for its objective and unbiased grading, which means you can trust that the characteristics of your diamond have been evaluated with the highest precision. This gives you confidence that the quality represented in the report matches the actual characteristics of the diamond.
While you might occasionally come across diamonds under 1 carat with a GIA Diamond Grading Report, it’s more common for larger diamonds. For smaller diamonds, GIA typically issues the Diamond Dossier, which provides a slightly less detailed assessment but is still highly reliable.
GIA Diamond Dossier


The GIA Diamond Dossier is typically issued for diamonds that are smaller than 1 carat. While it doesn’t include all the details found in the full GIA Diamond Grading Report, it still provides critical information about the diamond’s quality. The Dossier includes the 4C’s: Carat weight, Color, Clarity, and Cut—all graded according to GIA’s strict, industry-leading standards.
One key difference between the GIA Diamond Dossier and the Grading Report is that the Dossier does not include a detailed diagram marking the location of inclusions or blemishes. However, this does not compromise the Dossier’s reliability. Each GIA Diamond Dossier still provides an accurate assessment of the diamond’s characteristics, making it an essential tool for ensuring quality, especially for smaller diamonds.
The Dossier also includes a laser inscription of the GIA report number on the diamond’s girdle. This inscription matches the details on the certificate and allows you to verify the diamond’s authenticity by checking the GIA website. This feature is especially useful if the certificate is ever misplaced, as you can always match the diamond to its report using the inscription.
Update: As of April 9, 2023, GIA resumed issuing hardcopy paper certificates after initially transitioning to digital-only reports. This decision was reversed, allowing customers to continue receiving physical Dossiers with their diamond purchases. However, digital versions of the Dossier are still accessible for those who received them during the digital period.
The GIA Diamond Dossier remains a trusted certification for diamonds under 1 carat, offering the same level of precision and objectivity for smaller stones as the full Grading Report does for larger diamonds.
How to Read a GIA Certification
Before we dive in, it’s important to know that GIA (Gemological Institute of America) invented the 4C’s of Diamonds—the standard method for grading diamonds globally. Their grading system has become the benchmark for diamond certification and is widely adopted by other institutions. Once you learn how to read a GIA certification, you’ll be able to interpret reports from other institutions with ease, as they follow similar principles.
When reviewing a GIA certification, there are a few key sections you should pay attention to. Each one provides valuable insights into the unique characteristics of your diamond.
GIA Diamond Report:
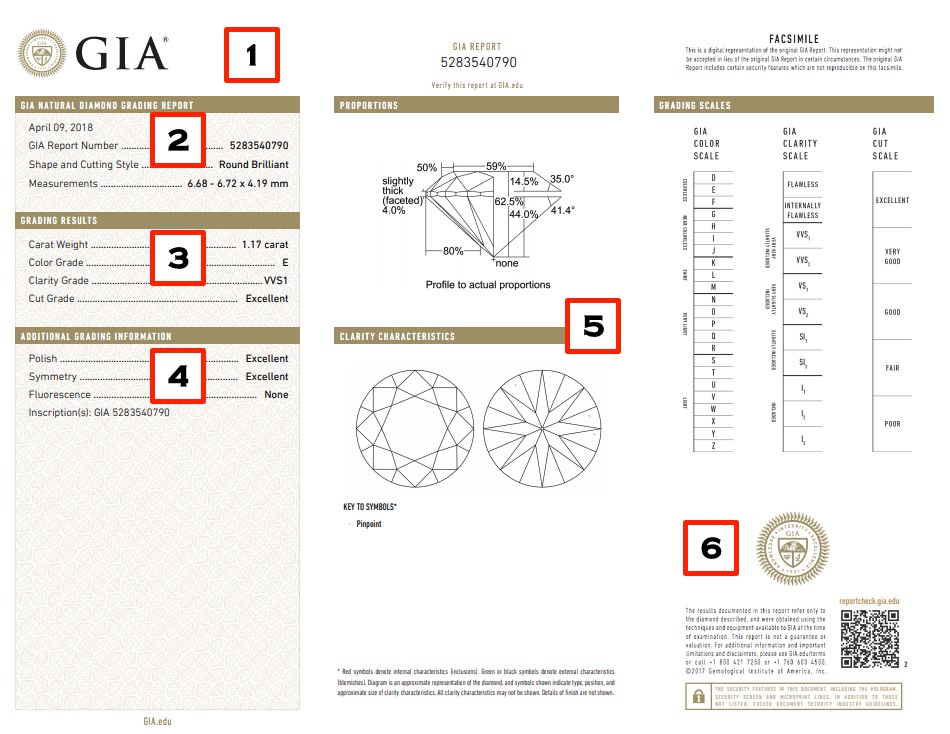

1. Upper Section: The Name of the Institution


The first thing you should check at the top of the report is the name of the institution that issued the certification. This is critical because the grading standards and reputation of the institution directly affect the reliability of the report.
For example, a diamond certified by GIA (Gemological Institute of America) carries more weight because GIA is known for its strict, impartial grading practices. Established in 1931, GIA is a nonprofit organization that set the standard for diamond grading and created the globally recognized 4C’s system (Carat, Cut, Color, and Clarity). The institution’s name at the top of the report signals that the diamond has been graded under these high standards, offering you a trustworthy and transparent evaluation.
Another widely recognized institution is HRD (Hoge Raad voor Diamant), which was established in 1973 in Belgium. HRD is also renowned for its grading accuracy, especially in Europe. Diamonds graded by HRD are sealed in secure plastic containers, ensuring their protection until they reach the customer.
However, GIA certifications are generally considered the gold standard worldwide and are often more sought after in the market, sometimes giving a GIA-graded diamond a premium value over diamonds certified by other institutions. For this reason, GIA-certified diamonds typically have higher resale value and are more widely accepted in international markets.
In contrast, diamonds graded by lesser-known or local institutions may not follow as stringent a grading process, and the accuracy of their reports can vary. For this reason, a diamond without a GIA or HRD certification may have discrepancies in its grading, which could lead to a mismatch between its quality and price.
Therefore, always ensure the diamond report comes from a reputable institution like GIA or HRD. This will give you confidence in the accuracy of the grading and the value of your diamond.
2. GIA Report Number, Shape, Cutting Style, and Measurements


- Report Number: Every GIA-certified diamond has a unique report number that is also laser-inscribed on the diamond’s girdle. You can use this number to verify your diamond’s details on GIA’s website.
- Shape and Cutting Style: This section describes the diamond’s shape (e.g., Round Brilliant) and cutting style (e.g., Brilliant Cut, Step Cut).
- Measurements: The diamond’s exact dimensions are provided here in millimeters (length, width, and depth). These precise measurements help determine how well the diamond is proportioned, which plays a key role in how light interacts with the stone.
You can always verify the Report Number and additional details on the GIA website:
Shape, Cutting Style, and Measurements
In this section, you’ll find details about the diamond’s shape, cutting style, and exact measurements in millimeters. The most popular shape is “Round Brilliant.”
3. The Essence: 4C’s of Diamonds


Carat

Carat refers to the weight of the diamond. One carat equals 0.2 grams, and diamonds are often referred to in points (e.g., a 50-point diamond is 0.50 carats). The more carats, the larger the diamond.
Color
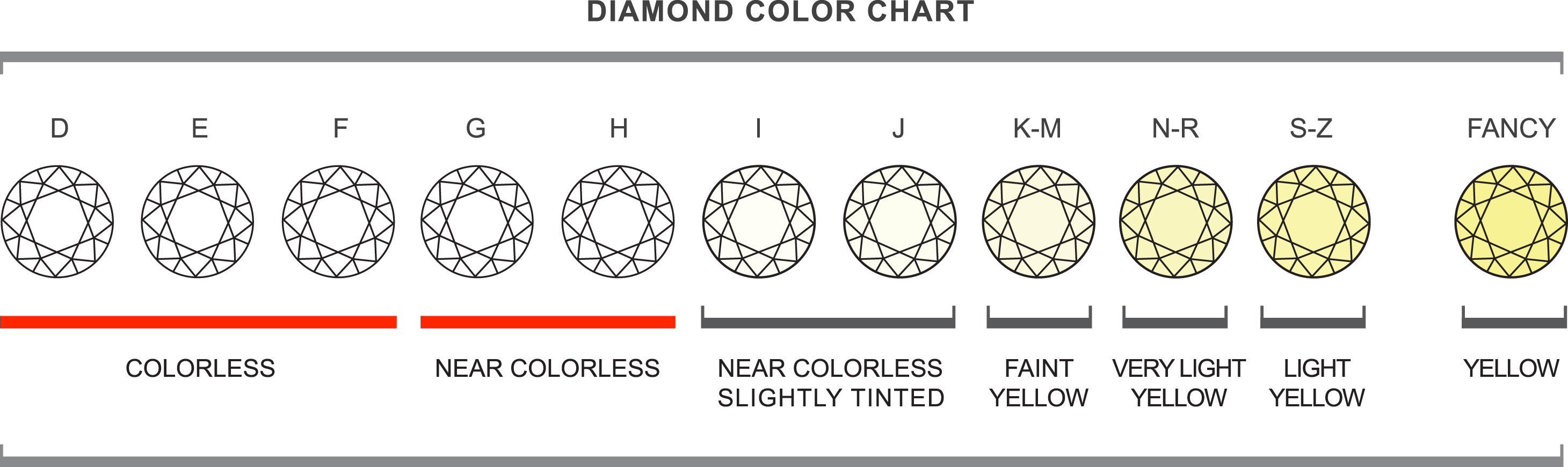

Color measures the degree to which a diamond is colorless. Graded from D (colorless) to Z (yellowish), D-grade diamonds are the most valuable due to their perfect lack of color.
Clarity
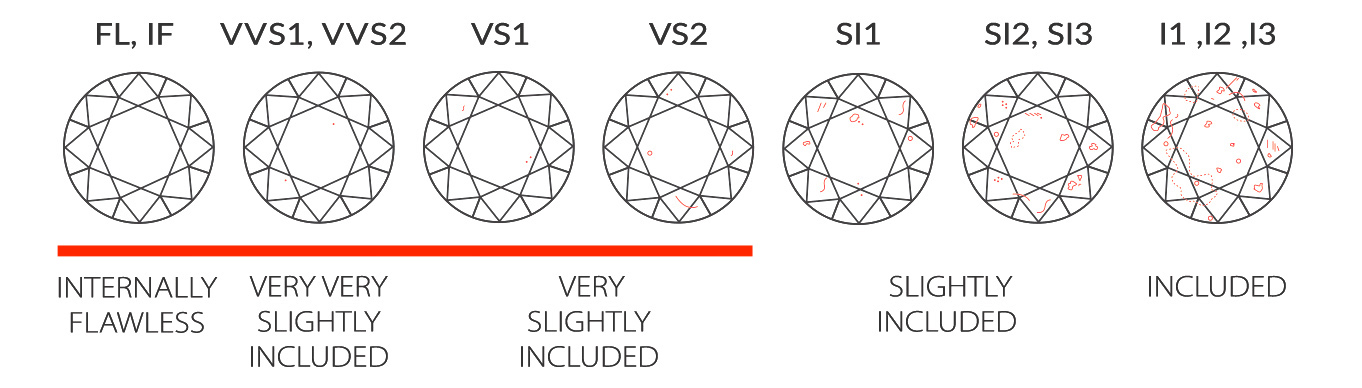

Clarity refers to the absence of internal or external flaws. Diamonds graded VVS1/2 or VS1/2 offer a balance of quality and price, as they have minimal inclusions that are difficult to detect with the naked eye.
Cut
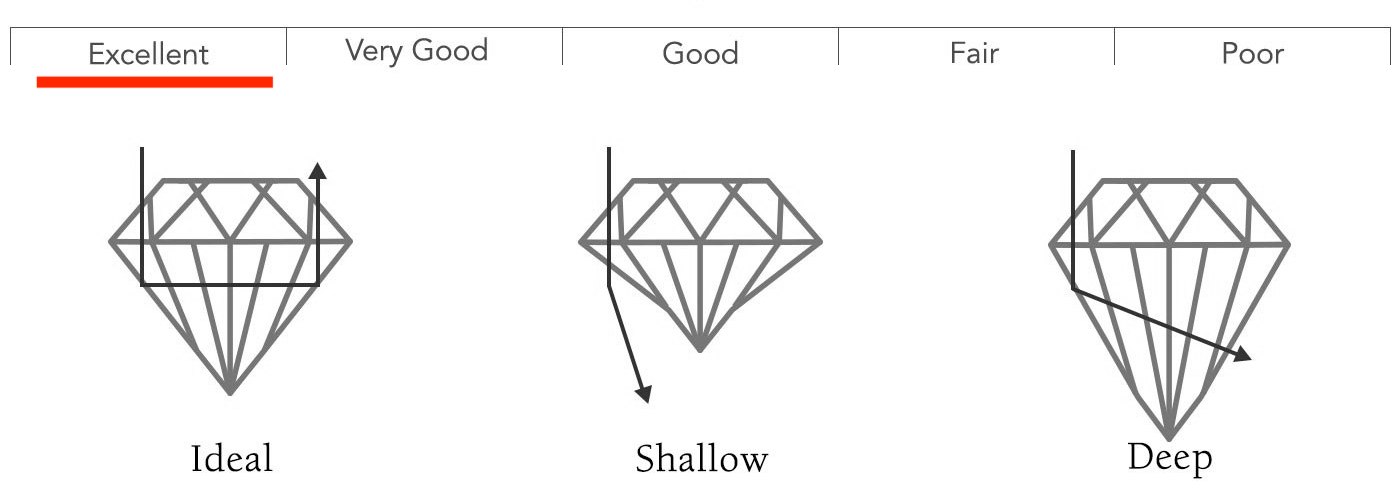

Cut is the most important factor for a diamond’s brilliance. A well-cut diamond will reflect light beautifully, enhancing its sparkle.
4. Additional Information and Comments


Polish describes how smooth the diamond’s surface is. The smoother it is, the better it reflects light.
Symmetry measures how perfectly aligned the facets are. Symmetrical diamonds reflect light more effectively.
Fluorescence


Fluorescence refers to a diamond’s reaction to UV light. Diamonds with fluorescence often display a blue tint, which some buyers prefer to avoid.
Read more: What is ‘diamond fluorescence’ and is it good or bad?
Inscription


This section details the laser inscription on your diamond, usually the GIA number, which you can use to verify the diamond’s identity.
Read more: What are ‘hearts and arrows’ diamonds?
Comments
This section may provide additional notes about the diamond’s clarity or shape, though it’s usually not as critical.
5. Proportions and Clarity Characteristics
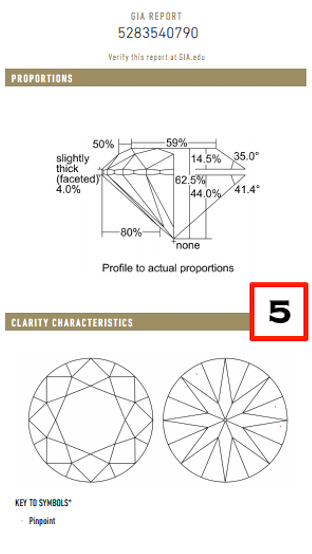

Proportions
In this section, the GIA report details the diamond’s proportions, expressed as percentages. These include the Table % (width), Depth %, various angles, and the Girdle Thickness. Understanding these proportions is key to assessing a diamond’s brilliance and how well it reflects light.
The Table % refers to the width of the diamond’s top surface, or “table.” Based on our experience, we recommend a Table % between 54% and 60%. This range is ideal for achieving balance and maximum light reflection. A Table % below this range may make the diamond appear smaller, while a larger table could reduce its sparkle.
In addition, make sure to check the Culet, the small point at the bottom of the diamond. A culet listed as “None” is preferred, as a larger culet can cause light leakage, diminishing the diamond’s brilliance.
Clarity Characteristics
The Clarity Characteristics section of the report is where you can learn about any inclusions (internal flaws) or blemishes (external flaws) within the diamond. These imperfections are mapped on a Clarity Plot diagram, helping to illustrate the unique features of your diamond.
Inclusions are internal flaws such as crystals, clouds, or needles. These inclusions occur naturally as the diamond forms. The GIA report marks these in red on the plot.
Blemishes are external surface flaws, like scratches or nicks. These are shown in green on the clarity plot. While some blemishes can be polished away, others are permanent.
Each diamond’s clarity is unique, much like a fingerprint. When reviewing clarity, it’s important to note the position of inclusions and blemishes. Inclusions on the edges can often be hidden by the setting, while those near the diamond’s table (top) are more visible and may affect the diamond’s overall appearance.
Read more: Clarity characteristics: tips only known by experts
Good VVS/VS: Things You Should Not Overlook
Not all VVS or VS diamonds are the same, even within the same clarity grade. Some diamonds within these grades have flaws that are barely noticeable and well-placed, while others may have inclusions located in more visible areas, like the table (the flat surface on the top of the diamond), which can negatively impact the diamond’s appearance. Here are some tips on what to look for.
- Inclusions in less visible areas: A “Good VVS” or “Good VS” diamond has inclusions located in less noticeable places, like near the edges or hidden beneath the crown facets. These inclusions are typically less likely to be seen, even under 10x magnification, and will not affect the beauty of the diamond once set in a piece of jewelry.
- Avoid inclusions on the table: Inclusions located on the table are more easily visible to the naked eye, especially if the diamond has a lower clarity grade within the VVS or VS range. These types of inclusions can detract from the diamond’s overall brilliance and sparkle, making the stone look less desirable.
At Above Diamond, we meticulously hand-select diamonds to ensure that any inclusions are located in places that will not detract from the beauty of the stone. We specialize in offering Good VVS and Good VS diamonds, where the inclusions are difficult to detect even under magnification. This ensures that the diamonds we provide are as close to flawless as possible to the naked eye, maximizing their brilliance and beauty.
Even though VVS and VS diamonds are not completely free of inclusions, diamonds with inclusions in the right places can still appear eye-clean and beautiful. This is why our process of selecting diamonds focuses not only on the clarity grade itself but also on the placement of the inclusions, ensuring that each diamond we offer meets our high standards of beauty and brilliance.
6. Security Marks
Lastly, check for GIA’s gold security seal, which ensures the report is authentic.


Conclusion: Diamond Reports Help You Buy with Confidence
By now, you should have a much clearer understanding of the importance of diamond certifications and how to read a GIA report. When buying a diamond, it’s not just about choosing a high color grade or a Triple Excellent cut. There are many additional factors—such as fluorescence, proportions, and clarity characteristics—that can significantly affect the diamond’s overall beauty and value.
A certified diamond provides you with detailed insight into these qualities, allowing you to make a well-informed decision. You’ll know exactly what you’re purchasing, and you can be confident that the diamond has been evaluated by experts according to the highest standards.
At Above Diamond, we take pride in ensuring that each diamond we offer meets the most stringent industry criteria. We don’t just rely on the 4C’s alone—we go beyond to select diamonds that possess exceptional brilliance, symmetry, and proportion, all while ensuring that inclusions are minimal and strategically placed to enhance the diamond’s natural beauty.
Ultimately, a diamond certification is your key to understanding the unique characteristics of your diamond. It gives you peace of mind, knowing that the diamond you choose will retain its value and beauty for a lifetime. With the right knowledge, you’ll not only find a stunning diamond but also invest in something that reflects your personal taste and style.
If you have any further questions on reading a diamond report, or if you need guidance in selecting the perfect diamond, feel free to contact us. We are here to assist you in making an informed and confident choice.